After a motor vehicle accident in New York or New Jersey, you could suffer injuries without realizing it. Depending on the force of the collision and if you hit your head on something, you could suffer a head injury. No-Fault Doctors specializes in the treatment of head injury, but first, we want to help our patients understand if they have a head injury. So, how long after a head injury can symptoms occur, and what symptoms should you look for? We explore the topic with a deep-dive guide we hope answers all your questions and eases your anxieties.
Understanding Head Injury
Before breaking down various head injuries, we want to explain the injury. When trauma damages the skull, scalp or brain, a person may develop a head injury.
Those who engage in recreational activities or play sports may consider head trauma the price of their favorite pastime, but a blow to the skull is not something to brush off. Without help from a neurologist and other medical professionals in New York or New Jersey, a head injury may cause mental impairment or permanent disability. Some people even die from head trauma.
Head trauma that affects the brain is a traumatic brain injury (TBI). Depending on the severity of the harm suffered, TBI patients could experience complications. Examples of altered states of consciousness a brain injury could trigger include loss of consciousness, concussion symptoms, coma, vegetative state, and brain death. Physical complications include infections, blood vessel damage, vertigo and seizures.
Types of Head Injuries
Aside from determining whether you have a head injury, another reason to see a neurologist after a motor vehicle collision is so you know what kind of head trauma you have. Concussions are the most prevalent head injury, happening when the brain bounces off the skull because of shaking or jarring. Even then, a person need not receive a blow to the head to sustain a concussion; getting hit somewhere else on the body could prove sufficient to jar or shake the brain. This head injury ranges from mild to severe.
Intracranial hematoma is brain bleeding beneath the skull. The head trauma forms a clot and ranges from mild to severe. Medical professionals group intracranial hematomas according to where they appear.
A contusion is a head injury that manifests as a bruise on the brain. It could cause inflammation and bleeding.
A Skull fracture happens when broken skull bones affect the brain. Damaged pieces of skull bone could slice into the brain and harm it.
Symptoms of Head Injury
A person with a head injury may experience various psychological and physical symptoms. Sometimes, symptoms appear soon after a car accident or another traumatic event, but they could take several days or weeks to appear, making it critical to see a medical professional as quickly as possible for an accurate diagnosis.
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
Physical symptoms of a mild traumatic brain injuries include:
- Loss of balance or dizziness
- Headache
- Vomiting or nausea
- Trouble speaking
- Sleepiness or fatigue
Anyone who displays the above symptoms may need professional treatment of head injury from a neurosurgeon.
Mental, cognitive, and behavioral symptoms of mild TBI include:
- Sleeping more than usual
- Blacking out anywhere from several seconds to several minutes
- Remaining conscious, but feeling disoriented or dazed
- Problems focusing or remembering things
- Mood swings or mood shifts
- Trouble sleeping
Mild TBIs may also cause anxiety and depression.
Sensory symptoms of mild brain trauma range from light or sound sensitivity to blurred vision, foul taste in the mouth, tinnitus, and other sensory problems.
Moderate-to-Severe TBI
Moderate-to-severe brain injuries share the same symptoms as mild brain injuries, but new symptoms could appear within the initial hours or days after the traumatic event. Physical signs include:
- Blacking out for several minutes or hours
- Chronic or worsening headache
- Repeatedly feeling nauseated or vomiting
- Seizing or convulsing
- Clear fluid draining from the ears or nose
- Dilation in one or both pupils
- Trouble waking up
- Numbness or weakness in the extremities
A moderate or severe TBI could also trigger a loss of balance.
Mental and cognitive indications of a moderate-to-severe brain injury include:
- Slurred speech
- Intense disorientation
- Odd behavior, such as becoming unusually agitated or aggressive
A more intense TBI may also cause distorted facial features.
Diagnosing Head Injury
Even if you display symptoms of head trauma, it makes sense to ensure you have a head injury and not another condition. Medical care providers may use the Glasgow Coma Scale as part of their initial assessment. The diagnostic method measures your ability to follow directions, speak coherently, and move your limbs and eyes. You receive a score between three and 15 on the scale, with lower scores indicating more severe brain injuries.
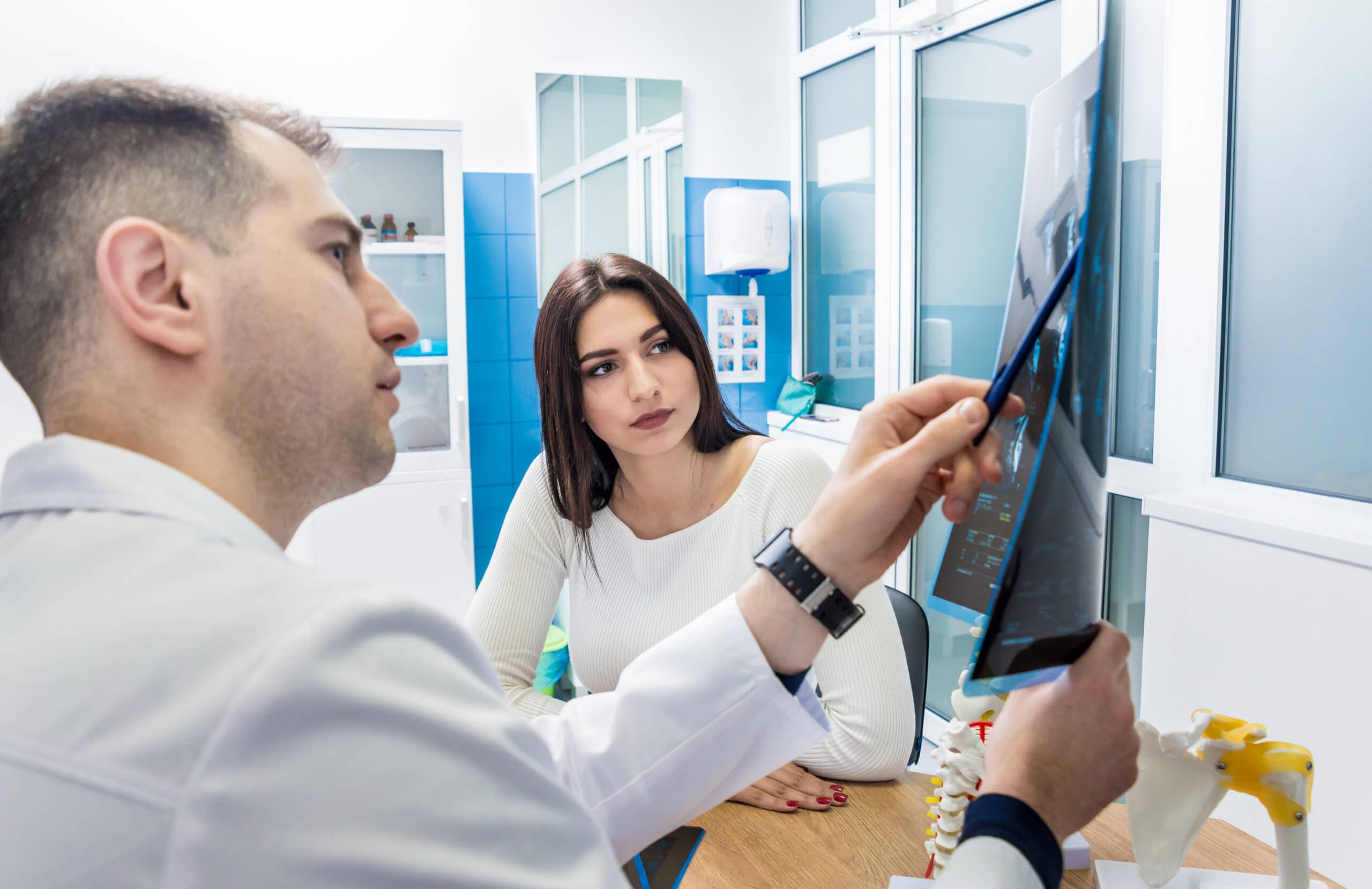

Doctors also gather information about the traumatic event to diagnose head injuries. If someone saw the car accident, she or he could help diagnose you by answering questions about how the incident happened, if you blacked out and for how long, and if the accident whipped your body around.
Health care professionals also use imaging tests to diagnose TBIs. Computerized tomography (CT) scans use X-rays to create an in-depth image of your brain to pinpoint brain bleeds, blood clots, bruised brain tissue, and brain tissue inflammation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) tests combine magnets and radio waves to build detailed pictures of your brain. You may not receive an MRI until after your condition stabilizes.
Aside from diagnosing your injury, your medical team could also want to monitor your brain. You may require an intracranial pressure monitor inserted in your skull with a probe to monitor tissue inflammation that increases pressure in your skull.
Treatment of Head Injury
If a physician diagnoses you with a head injury, you likely want to know what to expect for your head injury treatment.
Mild Head Injury
For mild head injuries, you may need nothing more than over-the-counter pain medication and rest to recover. You could also need someone to watch over you to help identify worsening, new or continuing symptoms. Ask your physician when you may resume your normal activities and how to juggle getting sufficient rest with not resting fully from physical and mental activity.
Emergency Medical Care
If diagnosed with a moderate-to-severe injury, you need immediate medical attention from a neurosurgeon to help ensure you have enough blood, protect your blood pressure, keep your oxygen levels up, and better ensure your injury does not worsen. A person involved in a car accident may have other harm to address besides a TBI. Supplementary medical treatment of head injury often focuses on addressing bleeding, swelling and low oxygen levels in the brain.
Prescription Medication
Sometimes, medical care providers recommend medications to treat brain trauma. If the brain cannot provide brain cells with oxygen and nutrients because of compressed blood vessels, doctors may use medication to put the patient into a medically induced coma. Comatose brains require only a little oxygen.
A moderate-to-severe brain injury could put a person at risk of suffering seizures for the initial week after sustaining a head injury. TBI patients could take anti-seizure drugs to protect their brains. If seizures continue after the first week, the person may stay on anti-seizure medication.
To increase urine output while reducing fluid in the tissues, medical care providers may prescribe diuretics. Intravenous diuretics help brain injury patients control the pressure inside the skull.
Medical Procedure
A neurologist would recommend emergency surgery to protect brain tissue and address various issues. For instance, medical procedures help resolve blood clots outside the brain caused by brain bleeds that harm healthy tissue and increase brain pressure.
Surgery also helps stitch skull fractures, remove skull fractures from the brain and stop bleeding in the brain. To ease pressure in the skull, surgeons may open a window in the skull to drain cerebrospinal fluid or make room for inflamed tissues.
Rehabilitation
Most individuals who suffer head injuries require rehabilitation as part of their treatment plan to relearn fundamental skills, such as talking or walking. Rehab often starts at the hospital before the patient transfers to a residential treatment facility, inpatient rehabilitation unit or outpatient services. How long rehabilitation lasts and the treatment a person needs depends on the part of the brain that sustained trauma and the severity of the harm.
Aside from wondering how long after a head injury can symptoms occur, you may also wonder which medical professionals help with the treatment of head injury. A psychiatrist could oversee your entire rehabilitation, prescribing necessary medication and helping you navigate rehab issues. If you need help to relearn or improve everyday skills or relearning movement patterns, you could work with an occupational or physical therapist.
Contact No-Fault Doctors Today

You deserve competent, trusted medical attention after a New York car accident, no matter how major or minor. If you have treatment of head injury questions, contact a No-Fault Doctors representative. We provide a free directory of New Jersey and New York medical professionals experienced with treating car collision victims, all of whom accept PIP and no-fault insurance. Call us day or night at 888-970-5065. If you prefer, fill out and submit an online form.
Sources:
https://www.webmd.com/fitness-exercise/guide/head-injuries-causes-and-treatments
